In recent years, Artificial Intelligence has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping industries, enhancing productivity, and influencing daily life in unprecedented ways. AI is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. This enables them to perform tasks like learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. From virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles, it is driving technological advancements and unlocking new opportunities. This blog explores the essence of Artificial Intelligence, its types, applications, and its transformative impact on the world.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
It is a revolutionary field of computer science that enables machines to mimic human intelligence. At its most basic level, it refers to the ability of machines to process information, recognize patterns, and adapt their responses to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional programming, where actions are explicitly coded and the outcome is known, Artificial Intelligence leverages algorithms to learn and improve from data over time, offering immense flexibility and accuracy.
AI is not limited to a single technology but encompasses a range of techniques, algorithms, and systems designed to solve complex problems. It is also not confined to a single domain or application. It spans diverse areas, including speech recognition, image processing, and robotics, making it one of the most versatile and impactful technology of the 21st century. Furthermore, it is the driving force behind many of the technologies we rely on daily.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
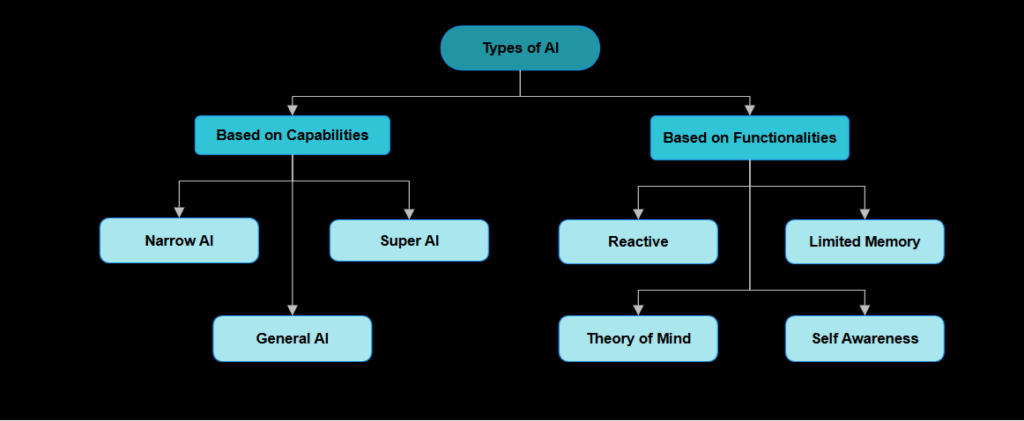
Artificial Intelligence can be divided into various categories based on its capabilities.
1. Narrow/Weak AI
These are systems specifically designed to carry out particular tasks. They function within set parameters and do not possess general intelligence. Examples include:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Recommendation algorithms used by Netflix and Amazon
- Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa
2. General/Strong AI
This seeks to replicate human intelligence across a wide range of tasks and fields. It remains a theoretical concept and has not yet been achieved. Such systems would:
- Understand and learn any intellectual task a human can perform
- Adapt to new environments without explicit programming
3. Superintelligent AI
This describes a theoretical future system that exceeds human intelligence in every aspect. Despite its vast potential, it brings significant ethical and safety challenges.
Artificial Intelligence can be divided into four categories based on its functions.
1. Reactive Machines
It are the most basic type of AI systems. It can only react to current scenarios and lacks the ability to store memories or learn from past experiences. These are task-specific and operate solely on real-time data. A notable example is IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer.
2. Limited Memory
It can store and use past data for a short duration to make decisions unlike reactive machines. It is commonly found in technologies like autonomous vehicles, which needs to analyze recent movement data to predict and navigate effectively.
3. Theory of Mind
It refers to an advanced concept where systems are capable of understanding emotions, beliefs, and intentions. These systems aim to interact with humans more naturally by recognizing and responding to mental states. Although still in the research phase, it has a great scope for social robotics and advanced communication tools.
4. Self-Aware
It represents the most sophisticated form of Artificial Intelligence. They possess a sense of self and consciousness, enabling them to understand their own existence and emotions. This is purely hypothetical at this point in time, but it could revolutionize various fields but also raises significant ethical and philosophical concerns.
Key Technologies Powering AI
AI systems rely on several foundational technologies and concepts, including:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
It is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that enable machines to learn from data. Key techniques include:
- Supervised Learning: Involves training models on labeled data
- Unsupervised Learning: Involves identifying patterns in unlabeled data
- Reinforcement Learning: Includes learning through trial and error
2. Deep Learning (DL)
It is a specialized branch of ML that uses neural networks to process large datasets. Neural networks are artificial models that mimic the human brain, enabling them to identify patterns and learn from data. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that process input data to make predictions or classifications. Through training, these networks adjust their connections to enhance performance in tasks like image recognition and language processing.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This technology enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Some applications that leverages NLP are Language translation, Chatbots and virtual assistants and sentiment analysis.
4. Computer Vision (CV)
It focuses on enabling machines to interpret and analyze visual information like images and videos. Some applications that use CV are medical image analysis, facial recognition and object detection.
Applications of AI
AI has permeated virtually every industry, driving innovation and improving efficiency. Some notable applications from various sectors include:
1. Healthcare
- Supporting disease diagnosis through image recognition.
- Personalizing treatment plans for patients
- Enabling remote patient monitoring
2. Finance
- Customer service automation
- Algorithmic trading
- Fraud detection
3. Retail
- Predictive analytics to forecast demand of products
- Providing personalized recommendations to improve customer Experience
- Optimizing inventory management and Logistics
4. Education
- Adaptive learning platforms
- Automated grading systems
- Virtual tutors
5. Transportation
- Autonomous vehicles
- Traffic management solutions
- Predictive maintenance for fleets
6. Entertainment
- Personalized content recommendations
- Realistic video game characters
7. Agriculture
- Monitoring crop health using drones
- Optimizing irrigation systems
- Predicting weather patterns
Benefits of AI
- Increased Efficiency : Automating repetitive tasks saves time and reduces errors.
- Increased Accuracy : It has improved the quality and correctness of a task.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-driven analytics provide valuable insights.
- Cost Reduction: AI reduces operational costs by streamlining processes in various industries.
- Personalization: AI tailors experiences and outcomes to individual preferences.
- Innovation: AI fosters creativity by enabling new solutions to complex problems.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
1. Job Displacement : The automation of tasks may lead to unemployment in certain sectors. Preparing the workforce for an AI-driven future is crucial.
2. Bias and Fairness : AI systems can adopt biases from their training data, resulting in unjust outcomes. It is crucial to ensure fairness and transparency.
3. Privacy Concerns : AI applications frequently depend on vast amounts of data, which raises concerns regarding data security and user privacy.
4. Ethical Dilemmas : The development of AI raises ethical questions, such as Who is responsible for AI’s actions? and How can we prevent misuse of AI technologies?
5. Safety Risks : Advanced AI systems may present risks if not adequately regulated, especially in fields such as autonomous weapons and superintelligent AI.
The Future of AI
As AI evolves, its influence on society will increase. Future trends in AI include:
- AI and IoT Integration: Merging AI with the Internet of Things to create smarter devices and systems that can automate and optimize processes.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Improving the transparency of AI decision-making processes, making it easier for users to understand how AI reaches conclusions.
- Personalized AI: Designing AI systems that can adjust to the unique needs and preferences of individual users, offering more tailored experiences.
- Regulation and Governance: Establishing frameworks to ensure the ethical development and application of AI, addressing concerns about safety and fairness.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is not just a technological breakthrough; it is a transformative force shaping the future. With applications spanning healthcare to entertainment, AI offers vast opportunities to enhance our lives. However, unlocking its full potential demands a responsible approach to addressing its challenges and ethical concerns.
As we delve deeper into the possibilities of Artificial Intelligence, it is essential to adopt a balanced approach that leverages its benefits while mitigating its risks. Embracing AI with an open mind and a cautious outlook will pave the way for a brighter, smarter future.
